Taiwan
In 1895, military defeat forced China’s Qing Dynasty to cede Taiwan to Japan. Taiwan came under Chinese Nationalist control after World War II. Following the communist victory on the mainland in 1949, 2 million Nationalists fled to Taiwan and established a government using the 1947 constitution drawn up for all of China. Beginning in the 1950s, the ruling authorities gradually democratized and incorporated the local population within the governing structure. This process expanded rapidly in the 1980s.
In 2000, Taiwan underwent its first peaceful transfer of power from the Nationalist (Kuomintang or KMT) to the Democratic Progressive Party. Throughout this period, the island prospered and became one of East Asia’s economic “Tigers.” The dominant political issues continue to be management of sensitive relations between Taiwan and China – specifically the question of Taiwan’s eventual status – as well as domestic priorities for economic reform and growth.
Geography
Location:
Eastern Asia, islands bordering the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, South China Sea, and Taiwan Strait, north of the Philippines, off the southeastern coast of China
Geographic coordinates:
23 30 N, 121 00 E
Map references:
Southeast Asia
Area:
total: 35,980 sq km
country comparison to the world: 139
land: 32,260 sq km
water: 3,720 sq km
note: includes the Pescadores, Matsu, and Quemoy islands
Area – comparative:
slightly smaller than Maryland and Delaware combined
Land boundaries:
0 km
Coastline:
1,566.3 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
Climate:
tropical; marine; rainy season during southwest monsoon (June to August); cloudiness is persistent and extensive all year
Terrain:
eastern two-thirds mostly rugged mountains; flat to gently rolling plains in west
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: South China Sea 0 m
highest point: Yu Shan 3,952 m
Natural resources:
small deposits of coal, natural gas, limestone, marble, and asbestos
Land use:
arable land: 24%
permanent crops: 1%
other: 75% (2011)
Irrigated land:
NA
Total renewable water resources:
67 cu km (2011)
Natural hazards:
earthquakes; typhoons
volcanism: Kueishantao Island (elev. 401 m), east of Taiwan, is its only historically active volcano, although it has not erupted in centuries
Environment – current issues:
air pollution; water pollution from industrial emissions, raw sewage; contamination of drinking water supplies; trade in endangered species; low-level radioactive waste disposal
Environment – international agreements:
party to: none of the selected agreements because of Taiwan’s international status
Geography – note:
strategic location adjacent to both the Taiwan Strait and the Luzon Strait
People & Society
Nationality:
noun: Taiwan (singular and plural)
note: example – he or she is from Taiwan; they are from Taiwan
adjective: Taiwan (or Taiwanese)
Ethnic groups:
Taiwanese (including Hakka) 84%, mainland Chinese 14%, indigenous 2%
Languages:
Mandarin Chinese (official), Taiwanese (Min), Hakka dialects
Religions:
mixture of Buddhist and Taoist 93%, Christian 4.5%, other 2.5%
Population:
23,359,928 (July 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 52
Age structure:
0-14 years: 14% (male 1,683,381/female 1,575,789)
15-24 years: 13.4% (male 1,613,197/female 1,526,344)
25-54 years: 47.4% (male 5,539,606/female 5,539,654)
55-64 years: 12% (male 1,506,657/female 1,571,208)
65 years and over: 11.6% (male 1,301,420/female 1,502,672) (2014 est.)
Median age:
total: 39.2 years
male: 38.5 years
female: 39.9 years (2014 est.)
Population growth rate:
0.25% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 177
Birth rate:
8.55 births/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 216
Death rate:
6.97 deaths/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
Net migration rate:
0.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.89 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2014 est.)
Infant mortality rate:
total: 4.49 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 186
male: 4.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 4.06 deaths/1,000 live births (2014 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 79.84 years
country comparison to the world: 38
male: 76.72 years
female: 83.2 years (2014 est.)
Total fertility rate:
1.11 children born/woman (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 222
HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate:
NA
HIV/AIDS – people living with HIV/AIDS:
NA
HIV/AIDS – deaths:
NA
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 96.1%
male: NA
female: NA (2003)
Government
Country name:
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Taiwan
local long form: none
local short form: Taiwan
former: Formosa
Government type:
multiparty democracy
Capital:
name: Taipei
geographic coordinates: 25 02 N, 121 31 E
time difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Administrative divisions:
includes main island of Taiwan plus smaller islands nearby and off coast of China’s Fujian Province; Taiwan is divided into 14 counties (hsien, singular and plural), 3 municipalities (shih, singular and plural), and 5 special municipalities (chih-hsia-shih, singular and plural)
counties: Changhua, Chiayi, Hsinchu, Hualien, Kinmen, Lienchiang, Miaoli, Nantou, Penghu, Pingtung, Taitung, Taoyuan, Yilan, Yunlin
municipalities: Chiayi, Hsinchu, Keelung
special municipalities: Kaohsiung (city), New Taipei (city), Taichung (city), Tainan (city), Taipei (city)
note: Taiwan uses a variety of romanization systems; while a modified Wade-Giles system still dominates, the city of Taipei has adopted a Pinyin romanization for street and place names within its boundaries; other local authorities use different romanization systems; names for administrative divisions that follow are taken from the Taiwan Yearbook 2007 published by the Government Information Office in Taipei.
National holiday:
Republic Day (Anniversary of the Chinese Revolution), 10 October (1911)
Constitution:
previous 1912, 1931; latest adopted 25 December 1946, promulgated 1 January 1947, effective 25 December 1947; revised several times, last in 2005 (2013)
Legal system:
civil law system
International law organization participation:
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Suffrage:
20 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President MA Ying-jeou (since 20 May 2008); Vice President WU Den-yih (since 20 May 2012)
head of government: Premier JIANG Yi-huah (President of the Executive Yuan) (since 18 February 2013); Vice Premier MAO Chi-kuo (Vice President of the Executive Yuan) (since 18 February 2013)
cabinet: Executive Yuan – ministers appointed by president on recommendation of premier
(For more information visit the World Leaders website Opens in New Window)
elections: president and vice president elected on the same ticket by popular vote for four-year terms (eligible for a second term); election last held on 14 January 2012 (next to be held in January 2016); premier appointed by the president; vice premiers appointed by the president on the recommendation of the premier
election results: MA Ying-jeou elected president; percent of vote – MA Ying-jeou 51.6%, TSAI Ing-wen 45.6%, James SOONG Chu-ye 2.8%
Legislative branch:
unicameral Legislative Yuan (113 seats – 73 district members elected by popular vote, 34 at-large members elected on basis of proportion of islandwide votes received by participating political parties, 6 elected by popular vote among aboriginal populations; members to serve four-year terms); parties must receive 5% of vote to qualify for at-large seats
elections: Legislative Yuan – last held on 14 January 2012 (next to be held in January 2016)
election results: Legislative Yuan – percent of vote by party – KMT 44.6%, DPP 34.6%, TSU 9.0%, PFP 5.5%, others 6.3%; seats by party – KMT 64, DPP 40, PFP 3, TSU 3, NPSU 2, independent 1
Judicial branch:
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and approximately 100 judges organized into 8 civil and 12 criminal divisions, each with a division chief justice and 4 associate justices); Constitutional Court (consists of the court president, vice president, and 13 justices)
judge selection and term of office: both Supreme Court and Constitutional Court justices appointed by the president of the republic with the approval of the Legislative Yuan; Supreme Court justices appointed for life; Constitutional Court president, vice-president, and 8 grand justices serve 4-year terms and remaining justices serve 8-year terms
subordinate courts: high courts; district courts; hierarchy of administrative courts
Political parties and leaders:
Democratic Progressive Party or DPP [SU Tseng-chang]
Kuomintang or KMT (Nationalist Party) [MA Ying-jeou]
New Party [YOK Mu-ming]
Non-Partisan Solidarity Union or NPSU [LIN Pin-kuan]
People First Party or PFP [James SOONG Chu-ye]
Taiwan Solidarity Union or TSU [HUANG Kun-huei]
Political pressure groups and leaders:
environmental groups
independence movement
various business groups
note: debate on Taiwan independence has become acceptable within the mainstream of domestic politics on Taiwan; public opinion polls consistently show a substantial majority of Taiwan people supports maintaining Taiwan’s status quo for the foreseeable future; advocates of Taiwan independence oppose the stand that the island will eventually unify with mainland China; advocates of eventual unification predicate their goal on the democratic transformation of the mainland
International organization participation:
ADB, APEC, BCIE, ICC (national committees), IOC, ITUC (NGOs), WTO
Diplomatic representation in the US:
none; commercial and cultural relations with the people in the United States are maintained through an unofficial instrumentality, the Taipei Economic and Cultural Representative Office in the United States (TECRO), a private nonprofit corporation that performs citizen and consular services similar to those at diplomatic posts
representative: SHEN Lyu-shin (since 1 April 2014)
office: 4201 Wisconsin Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20016
telephone: [1] 202 895-1800
Taipei Economic and Cultural Offices (branch offices): Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Guam, Houston, Honolulu, Kansas City, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco, Seattle
Diplomatic representation from the US:
none; commercial and cultural relations with the people on Taiwan are maintained through an unofficial instrumentality, the American Institute in Taiwan (AIT), a private nonprofit corporation that performs citizen and consular services similar to those at diplomatic posts
director: Christopher J. MARUT
office: #7 Lane 134, Hsin Yi Road, Section 3, Taipei 106, Taiwan
telephone: [1] [886] (02) 2162-2000
FAX: [1] [886] (02) 2162-2251
other offices: Kaohsiung
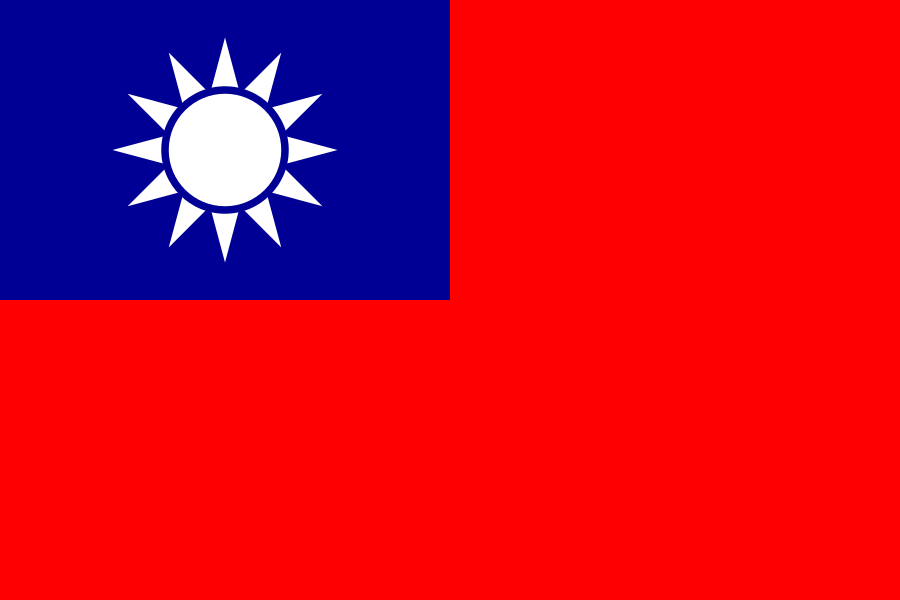
Flag description:
red field with a dark blue rectangle in the upper hoist-side corner bearing a white sun with 12 triangular rays; the blue and white design of the canton (symbolizing the sun of progress) dates to 1895; it was later adopted as the flag of the Kuomintang Party; blue signifies liberty, justice, and democracy; red stands for fraternity, sacrifice, and nationalism, white represents equality, frankness, and the people’s livelihood; the 12 rays of the sun are those of the months and the twelve traditional Chinese hours (each ray equals two hours)
National symbol(s):
white, 12-rayed sun on blue field
National anthem:
name: “Zhonghua Minguo guoge” (National Anthem of the Republic of China)
lyrics/music: HU Han-min, TAI Chi-t’ao, and LIAO Chung-k’ai/CHENG Mao-Yun
note: adopted 1930; the anthem is also the song of the Kuomintang Party; it is informally known as “San Min Chu I” or “San Min Zhu Yi” (Three Principles of the People); because of political pressure from China, “Guo Qi Ge” (National Banner Song) is used at international events rather than the official anthem of Taiwan; the “National Banner Song” has gained popularity in Taiwan and is commonly used during flag raisings
Economy
Economy – overview:
Taiwan has a dynamic capitalist economy with gradually decreasing government guidance of investment and foreign trade. Exports, led by electronics, machinery, and petrochemicals have provided the primary impetus for economic development. This heavy dependence on exports exposes the economy to fluctuations in world demand. Taiwan’s diplomatic isolation, low birth rate, and rapidly aging population are other major long-term challenges. Free trade agreements have proliferated in East Asia over the past several years, and following the landmark Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA) signed with China in June 2010, Taiwan in July 2013 signed a free trade deal with New Zealand—Taipei’s first-ever with a country with which it does not maintain diplomatic relations—and in November inked a trade pact with Singapore. Negotiations continue on follow-on components of ECFA regarding trade in goods and a dispute resolution mechanism; a trade in services agreement is under review in the legislature. Taiwan’s Total Fertility rate of just over one child per woman is among the lowest in the world, raising the prospect of future labor shortages, falling domestic demand, and declining tax revenues. Taiwan’s population is aging quickly, with the number of people over 65 accounting for 11.2% of the island’s total population as of 2012. The island runs a large overall trade surplus largely because of its surplus with China, and its foreign reserves are the world’s sixth largest, behind China, Japan, Saudi Arabia, Russia, and Switzerland. In 2006 China overtook the US to become Taiwan’s second-largest source of imports after Japan. China is also the island’s number one destination for foreign direct investment. Taiwan since 2009 has gradually loosened rules governing Chinese investment on the island, and has also secured greater market access for its investors in the mainland. In August 2012, Taiwan Central Bank signed a memorandum of understanding on cross-Strait currency settlement with its Chinese counterpart. The MOU allows for the direct settlement of Chinese RMB and the New Taiwan dollar across the Strait, which could help develop Taiwan into a local RMB hub. Closer economic links with the mainland bring greater opportunities for the Taiwan economy, but also poses new challenges as the island becomes more economically dependent on China while political differences remain unresolved.
GDP (purchasing power parity):
$926.4 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
$906.6 billion (2012 est.)
$894.7 billion (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$484.7 billion (2013 est.)
GDP – real growth rate:
2.2% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 138
1.3% (2012 est.)
4.1% (2011 est.)
GDP – per capita (PPP):
$39,600 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
$38,900 (2012 est.)
$38,500 (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
Gross national saving:
31.3% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 25
30.3% of GDP (2012 est.)
29.6% of GDP (2011 est.)
GDP – composition, by end use:
household consumption: 59.5%
government consumption: 12.2%
investment in fixed capital: 19.4%
investment in inventories: 0.3%
exports of goods and services: 73.1%
imports of goods and services: -64.5%
(2013 est.)
GDP – composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture: 2%
industry: 29.4%
services: 68.6% (2013 est.)
Agriculture – products:
rice, vegetables, fruit, tea, flowers; pigs, poultry; fish
Industries:
electronics, communications and information technology products, petroleum refining, chemicals, textiles, iron and steel, machinery, cement, food processing, vehicles, consumer products, pharmaceuticals
Industrial production growth rate:
1.8% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 129
Labor force:
11.55 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
Labor force – by occupation:
agriculture: 5%
industry: 36.2%
services: 58.8% (2012 est.)
Unemployment rate:
4.1% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
4.2% (2012 est.)
Population below poverty line:
1.5% (2012 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 6.4%
highest 10%: 40.3% (2010)
Distribution of family income – Gini index:
34.2 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 94
32.6 (2000)
Budget:
revenues: $78.24 billion
expenditures: $90.38 billion (2013 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
16.1% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-2.5% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
Public debt:
38.9% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
35.8% of GDP (2012 est.)
note: data for central government
Fiscal year:
calendar year
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
1.1% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
1.9% (2012 est.)
Central bank discount rate:
1.88% (31 December 2012)
country comparison to the world: 113
1.88% (31 December 2011)
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
2.9% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
2.88% (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of narrow money:
$450.1 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
$426.2 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of broad money:
$1.189 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
$1.152 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of domestic credit:
$753.5 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
$743.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Market value of publicly traded shares:
$831.9 billion (31 December 2012)
country comparison to the world: 17
$784.1 billion (31 December 2011)
$738.3 billion (31 December 2010)
Current account balance:
$56.66 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 9
$49.92 billion (2012 est.)
Exports:
$305.8 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 20
$299.8 billion (2012 est.)
Exports – commodities:
electronics, flat panels, machinery; metals; textiles, plastics, chemicals; optical, photographic, measuring, and medical instruments
Exports – partners:
China 27.1%, Hong Kong 13.2%, US 10.3%, Japan 6.4%, Singapore 4.4% (2012 est.)
Imports:
$268.5 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 19
$268.8 billion (2012 est.)
Imports – commodities:
electronics, machinery, crude petroleum, precision instruments, organic chemicals, metals
Imports – partners:
Japan 17.6%, China 16.1%, US 9.5% (2012 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$414.5 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$408.5 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Debt – external:
$146.8 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 38
$130.8 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of direct foreign investment – at home:
$62.94 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
$59.36 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of direct foreign investment – abroad:
$240.3 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
$226.1 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
Exchange rates:
New Taiwan dollars (TWD) per US dollar –
29.77 (2013 est.)
29.616 (2012 est.)
31.648 (2010 est.)
33.061 (2009)
31.53 (2008)