France
France today is one of the most modern countries in the world and is a leader among European nations. It plays an influential global role as a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, NATO, the G-8, the G-20, the EU and other multilateral organizations. France rejoined NATO’s integrated military command structure in 2009, reversing DE GAULLE’s 1966 decision to take French forces out of NATO.
Since 1958, it has constructed a hybrid presidential-parliamentary governing system resistant to the instabilities experienced in earlier, more purely parliamentary administrations. In recent decades, its reconciliation and cooperation with Germany have proved central to the economic integration of Europe, including the introduction of a common currency, the euro, in January 1999. In the early 21st century, five French overseas entities – French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion – became French regions and were made part of France proper.
Geography
Location:
metropolitan France: Western Europe, bordering the Bay of Biscay and English Channel, between Belgium and Spain, southeast of the UK; bordering the Mediterranean Sea, between Italy and Spain;
- French Guiana: Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Brazil and Suriname
- Guadeloupe: Caribbean, islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Puerto Rico
- Martinique: Caribbean, island between the Caribbean Sea and North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago
- Mayotte: Southern Indian Ocean, island in the Mozambique Channel, about half way between northern Madagascar and northern Mozambique
- Reunion: Southern Africa, island in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar
Geographic coordinates:
- metropolitan France: 46 00 N, 2 00 E
- French Guiana: 4 00 N, 53 00 W
- Guadeloupe: 16 15 N, 61 35 W
- Martinique: 14 40 N, 61 00 W
- Mayotte: 12 50 S, 45 10 E
- Reunion: 21 06 S, 55 36 E
Map references:
- metropolitan France: Europe
- French Guiana: South America
- Guadeloupe: Central America and the Caribbean
- Martinique: Central America and the Caribbean
- Mayotte: Africa
- Reunion: World
Area:
total: 643,801 sq km; 551,500 sq km (metropolitan France)
country comparison to the world: 43
land: 640,427 sq km; 549,970 sq km (metropolitan France)
water: 3,374 sq km; 1,530 sq km (metropolitan France)
note: the first numbers include the overseas regions of French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion
Area – comparative:
Area comparison map:
Land boundaries:
metropolitan France – total: 2,890.6 km
border countries: Andorra 56.6 km, Belgium 620 km, Germany 451 km, Italy 488 km, Luxembourg 73 km, Monaco 6 km, Spain 623 km, Switzerland 573 km
French Guiana – total: 1,183 km
border countries: Brazil 673 km, Suriname 510 km
Coastline:
total: 4,853 km
metropolitan France: 3,427 km
Maritime claims:
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm (does not apply to the Mediterranean)
continental shelf: 200 m depth or to the depth of exploitation
Climate:
- metropolitan France: generally cool winters and mild summers, but mild winters and hot summers along the Mediterranean; occasional strong, cold, dry, north-to-northwesterly wind known as mistral
- French Guiana: tropical; hot, humid; little seasonal temperature variation
- Guadeloupe and Martinique: subtropical tempered by trade winds; moderately high humidity; rainy season (June to October); vulnerable to devastating cyclones (hurricanes) every eight years on average
- Mayotte: tropical; marine; hot, humid, rainy season during northeastern monsoon (November to May); dry season is cooler (May to November)
- Reunion: tropical, but temperature moderates with elevation; cool and dry (May to November), hot and rainy (November to April)
Terrain:
- metropolitan France: mostly flat plains or gently rolling hills in north and west; remainder is mountainous, especially Pyrenees in south, Alps in east
- French Guiana: low-lying coastal plains rising to hills and small mountains
- Guadeloupe: Basse-Terre is volcanic in origin with interior mountains; Grande-Terre is low limestone formation; most of the seven other islands are volcanic in origin
- Martinique: mountainous with indented coastline; dormant volcano
- Mayotte: generally undulating, with deep ravines and ancient volcanic peaks
- Reunion: mostly rugged and mountainous; fertile lowlands along coast
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Rhone River delta -2 m
highest point: Mont Blanc 4,807 m
note: in order to assess the possible effects of climate change on the ice and snow cap of Mont Blanc, its surface and peak have been extensively measured in recent years; these new peak measurements have exceeded the traditional height of 4,807 m and have varied between 4,808 m and 4,811 m; the actual rock summit is 4,792 m and is 40 m away from the ice-covered summit
Natural resources:
- metropolitan France: coal, iron ore, bauxite, zinc, uranium, antimony, arsenic, potash, feldspar, fluorspar, gypsum, timber, fish
- French Guiana: gold deposits, petroleum, kaolin, niobium, tantalum, clay
Land use:
arable land: 33.45%
permanent crops: 1.86%
other: 64.69%
note: French Guiana – arable land 0.13%, permanent crops 0.04%, other 99.83% (90% forest, 10% other); Guadeloupe – arable land 11.70%, permanent crops 2.92%, other 85.38%; Martinique – arable land 9.09%, permanent crops 10.0%, other 80.91%; Reunion – arable land 13.94%, permanent crops 1.59%, other 84.47% (2011)
Irrigated land:
total: 26,420 sq km 26,950 sq km
metropolitan France: 27,230 sq km (2007)
Total renewable water resources:
211 cu km (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
total: 31.62 cu km/yr (19%/71%/10%)
per capita: 512.1 cu m/yr (2009)
Natural hazards:
metropolitan France: flooding; avalanches; midwinter windstorms; drought; forest fires in south near the Mediterranean
overseas departments: hurricanes (cyclones); flooding; volcanic activity (Guadeloupe, Martinique, Reunion)
Environment – current issues:
some forest damage from acid rain; air pollution from industrial and vehicle emissions; water pollution from urban wastes, agricultural runoff
Environment – international agreements:
party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Geography – note:
largest West European nation
People & Society
Nationality:
noun: Frenchman(men), Frenchwoman(women)
adjective: French
Ethnic groups:
Celtic and Latin with Teutonic, Slavic, North African, Indochinese, Basque minorities
overseas departments: black, white, mulatto, East Indian, Chinese, Amerindian
Languages:
French (official) 100%, rapidly declining regional dialects and languages (Provencal, Breton, Alsatian, Corsican, Catalan, Basque, Flemish)
overseas departments: French, Creole patois, Mahorian (a Swahili dialect)
Religions:
Roman Catholic 83%-88%, Protestant 2%, Jewish 1%, Muslim 5%-10%, unaffiliated 4%
overseas departments: Roman Catholic, Protestant, Hindu, Muslim, Buddhist, pagan
Population:
66,259,012
country comparison to the world: 22
note: the above figure is for metropolitan France and five overseas regions; the metropolitan France population is 62,814,233 (July 2014 est.)
Age structure:
0-14 years: 18.7% (male 6,337,877/female 6,053,185)
15-24 years: 11.9% (male 4,018,044/female 3,837,191)
25-54 years: 38.6% (male 12,851,278/female 12,719,073)
55-64 years: 18.3% (male 4,012,614/female 4,290,624)
65 years and over: 17.9% (male 5,197,519/female 6,941,607) (2014 est.)
Dependency ratios:
total dependency ratio: 57.4 %
youth dependency ratio: 28.6 %
elderly dependency ratio: 28.8 %
potential support ratio: 3.5 (2014 est.)
Median age:
total: 40.9 years
male: 39.3 years
female: 42.4 years (2014 est.)
Population growth rate:
0.45% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 158
Birth rate:
12.49 births/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 159
Death rate:
9.06 deaths/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 65
Net migration rate:
1.09 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
Urbanization:
urban population: 85.8% of total population (2011)
rate of urbanization: 1.1% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
Major urban areas – population:
PARIS (capital) 10.62 million; Marseille-Aix-en-Provence 14,890,100; Lyon 1.488 million; Lille 1.042 million; Nice-Cannes 991,000; Toulouse 933,000 (2011)
Sex ratio:
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.74 male(s)/female
total population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2014 est.)
Mother’s mean age at first birth:
28.1 (2010 est.)
Maternal mortality rate:
8 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)
country comparison to the world: 158
Infant mortality rate:
total: 3.31 deaths/1,000 live births
country comparison to the world: 214
male: 3.63 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.97 deaths/1,000 live births (2014 est.)
Life expectancy at birth:
total population: 81.66 years
country comparison to the world: 15
male: 78.55 years
female: 84.91 years (2014 est.)
Total fertility rate:
2.08 children born/woman (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
Contraceptive prevalence rate:
76.4%
note: percent of women aged 20-49 (2008)
Health expenditures:
11.6% of GDP (2011)
country comparison to the world: 10
Physicians density:
3.38 physicians/1,000 population (2011)
Hospital bed density:
6.6 beds/1,000 population (2010)
Drinking water source:
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2011 est.)
Sanitation facility access:
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2011 est.)
HIV/AIDS – adult prevalence rate:
0.4% (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 78
HIV/AIDS – people living with HIV/AIDS:
150,000 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
HIV/AIDS – deaths:
1,700 (2009 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
Obesity – adult prevalence rate:
18.2% (2008)
country comparison to the world: 108
Education expenditures:
5.9% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 43
Literacy:
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 99%
male: 99%
female: 99% (2003 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
total: 16 years
male: 16 years
female: 16 years (2011)
Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:
total: 23.8%
country comparison to the world: 43
male: 23.9%
female: 23.7% (2012)
Government
Country name:
conventional long form: French Republic
conventional short form: France
local long form: Republique francaise
local short form: France
Government type:
Republic
Capital:
name: Paris
geographic coordinates: 48 52 N, 2 20 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
note: applies to metropolitan France only, not to its overseas departments, collectivities, or territories
Administrative divisions:
27 regions (regions, singular – region); Alsace, Aquitaine, Auvergne, Basse-Normandie (Lower Normandy), Bourgogne (Burgundy), Bretagne (Brittany), Centre, Champagne-Ardenne, Corse (Corsica), Franche-Comte, Guadeloupe, Guyane (French Guiana), Haute-Normandie (Upper Normandy), Ile-de-France, Languedoc-Roussillon, Limousin, Lorraine, Martinique, Mayotte, Midi-Pyrenees, Nord-Pas-de-Calais, Pays de la Loire, Picardie, Poitou-Charentes, Provence-Alpes-Cote d’Azur, Reunion, Rhone-Alpes
note: France is divided into 22 metropolitan regions (including the “territorial collectivity” of Corse or Corsica) and 5 overseas regions (French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, and Reunion) and is subdivided into 96 metropolitan departments and 5 overseas departments (which are the same as the overseas regions)
Dependent areas:
Clipperton Island, French Polynesia, French Southern and Antarctic Lands, New Caledonia, Saint Barthelemy, Saint Martin, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Wallis and Futuna
note: the US does not recognize claims to Antarctica; New Caledonia has been considered a “sui generis” collectivity of France since 1998, a unique status falling between that of an independent country and a French overseas department
Independence:
no official date of independence: 486 (Frankish tribes unified under Merovingian kingship); 10 August 843 (Western Francia established from the division of the Carolingian Empire); 14 July 1789 (French monarchy overthrown); 22 September 1792 (First French Republic founded); 4 October 1958 (Fifth French Republic established)
National holiday:
Fete de la Federation, 14 July (1790); note – although often incorrectly referred to as Bastille Day, the celebration actually commemorates the holiday held on the first anniversary of the storming of the Bastille (on 14 July 1789) and the establishment of a constitutional monarchy; other names for the holiday are Fete Nationale (National Holiday) and quatorze juillet (14th of July)
Constitution:
4 October 1958 (French Constitution) (2013)
Legal system:
civil law; review of administrative but not legislative acts
International law organization participation:
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Suffrage:
18 years of age; universal
Executive branch:
chief of state: President Francois HOLLANDE (since 15 May 2012)
head of government: Prime Minister Manuel VALLS (since 1 April 2014)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president at the suggestion of the prime minister
(For more information visit the World Leaders website Opens in New Window)
elections: president elected by popular vote for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 22 April and 6 May 2012 (next to be held in the spring of 2017); prime minister appointed by the president
election results: Francois HOLLANDE elected; first round: percent of vote – Francois HOLLANDE 28.6%, Nicolas SARKOZY 27.2%, Marine LE PEN 17.9%, Jean-Luc MELENCHON 11.1%, Francois BAYROU, 9.1%, others 6.1%; second round: HOLLANDE 51.6%, SARKOZY 48.4%
Legislative branch:
bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of the Senate or Senat (348 seats; 328 for metropolitan France and overseas departments, 2 for New Caledonia, 2 for French Polynesia, 1 for Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, 1 for Saint-Barthelemy, 1 for Saint-Martin, 1 for Wallis and Futuna, and 12 for French nationals abroad; members indirectly elected by an electoral college to serve six-year terms; one third elected every three years); and the National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (577 seats; 555 for metropolitan France, 15 for overseas departments, 7 for overseas dependencies; members elected by popular vote under a single-member majority system to serve five-year terms)
elections: Senate – last held on 25 September 2011 (next to be held in September 2014); National Assembly – last held on 10 and 17 June 2012 (next to be held in June 2017)
election results: Senate – percent of vote by party – NA; seats by party – PS/Greens 140, UMP 132, UDF 31, PCF/MRC 21, PRG 17, other 7; National Assembly – percent of vote by party – PS 48.5%, UMP 33.6%, miscellaneous left wing parties 3.8%, Greens 3.0%, miscellaneous right wing parties 2.6%, NC 2.1%, PRG 2.1%, FDG 1.7%, other 2.6%; seats by party – PS 280, UMP 194, miscellaneous left wing parties 22, Greens 17, miscellaneous right wing parties 15, NC 12, PRG 12, FDG 10, other 15
Judicial branch:
highest court(s): Court of Cassation or Cour de Cassation (consists of the court president, 6 divisional presiding judges, 120 trial judges, and 70 deputy judges organized into 6 divisions – 3 civil, 1 commercial, 1 labor, and 1 criminal); Constitutional Council (consists of 9 members)
judge selection and term of office: Court of Cassation judges appointed by the president of the republic from nominations from the High Council of the Judiciary, presided by the Court of Cassation and 15 appointed members; judge term of appointment NA; Constitutional Council members appointed – 3 by the president of the republic and 3 each by the National Assembly and Senate presidents; members serve 9-year, non-renewable terms with one third of the membership renewed every 3 years
subordinate courts: appellate courts or Cour d’Appel; regional courts or Tribunal de Grande Instance; first instance courts or Tribunal’ d’instance
Political parties and leaders:
Europe Ecology – The Greens or EELV [Emmanuelle COSSE]
French Communist Party or PCF [Pierre LAURENT]
Left Front Coalition or FDG [Jean-Luc MELENCHON]
Left Party or PG [Jean-Luc MELENCHON and Martine BILLARD]
Left Radical Party or PRG [Jean-Michel BAYLET] (previously Radical Socialist Party or PRS and the Left Radical Movement or MRG)
Movement for France or MPF [Philippe DE VILLIERS]
National Front or FN [Marine LE PEN]
New Anticapitalist Party or NPA [collective leadership; main spokesperson Christine POUPIN]
New Center or NC [Herve MORIN]
Radical Party [Jean-Louis BORLOO]
Rally for France or RPF [Charles PASQUA]
Republican and Citizen Movement or MRC [Jean-Luc LAURENT]
Socialist Party or PS [Haerlem DESIR]
United Republic or RS [Dominique DE VILLEPIN]
Union for a Popular Movement or UMP [Jean-Francois COPE]
Union des Democrates et Independants or UDI [Jean-Louis BORLOO] and Democratic Movement or MoDem [Francois BAYROU] (previously Union for French Democracy or UDF); together known as UDI-Modem
Worker’s Struggle (Lutte Ouvriere) or LO [collective leadership; spokespersons Nathalie ARTHAUD and Arlette LAQUILLER]
Political pressure groups and leaders:
Confederation Francaise Democratique du Travail (French Democratic Confederation of Labor) or CFDT, left-leaning labor union with approximately 875,000 members [Laurent BERGER, Secretary General]
Confederation francaise de l’encadrement – Confederation generale des cadres (French Confederation of Management – General Confederation of Executives) or CFE-CGC, independent white-collar union with 140,000 members [Carole COUVERT, president]
Confederation francaise des travailleurs chretiens (French Confederation of Christian Workers) or CFTC, independent labor union founded by Catholic workers that claims 142,000 members [Philippe LOUIS, president]
Confederation generale du travail (General Confederation of Labor) or CGT, historically communist labor union with approximately 710,000 members [Bernard THIBAULT, secretary general]
Confederation generale du travail – Force ouvriere (General Confederation of Labor – Worker’s Force) or FO, independent labor union with an estimated 300,000 members [Jean-Claude MAILLY, secretary general]
Mouvement des entreprises de France or MEDEF, employers’ union with 750,000 companies as members (claimed) [Pierre GATTAZ, president]
French Guiana:
conservationists
gold mining pressure groups
hunting pressure groups
- Guadeloupe:
Christian Movement for the Liberation of Guadeloupe or KLPG
General Federation of Guadeloupe Workers or CGT-G
General Union of Guadeloupe Workers or UGTG
Movement for an Independent Guadeloupe or MPGI
The Socialist Renewal Movement
- Martinique:
Caribbean Revolutionary Alliance or ARC
Central Union for Martinique Workers or CSTM
Frantz Fanon Circle
League of Workers and Peasants
Proletarian Action Group or GAP
- Reunion:
NA
International organization participation:
ADB (nonregional member), AfDB (nonregional member), Arctic Council (observer), Australia Group, BDEAC, BIS, BSEC (observer), CBSS (observer), CE, CERN, EAPC, EBRD, ECB, EIB, EITI (implementing country), EMU, ESA, EU, FAO, FATF, FZ, G-20, G-5, G-7, G-8, G-10, IADB, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD (partners), IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, InOC, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NATO, NEA, NSG, OAS (observer), OECD, OIF, OPCW, OSCE, Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club, PCA, PIF (partner), Schengen Convention, SELEC (observer), SPC, UN, UN Security Council, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, Union Latina, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNRWA, UNSC (permanent), UNTSO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO, ZC
Diplomatic representation in the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador Francois M. DELATTRE (since 18 February 2011)
chancery: 4101 Reservoir Road NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 944-6000
FAX: [1] (202) 944-6166
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New Orleans, New York, San Francisco
Diplomatic representation from the US:
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d’Affaires Mark A. TAPLIN; note – also accredited to Monaco
embassy: 2 Avenue Gabriel, 75382 Paris Cedex 08
mailing address: PSC 116, APO AE 09777
telephone: [33] (1) 43-12-22-22
FAX: [33] (1) 42 66 97 83
consulate(s) general: Marseille, Strasbourg
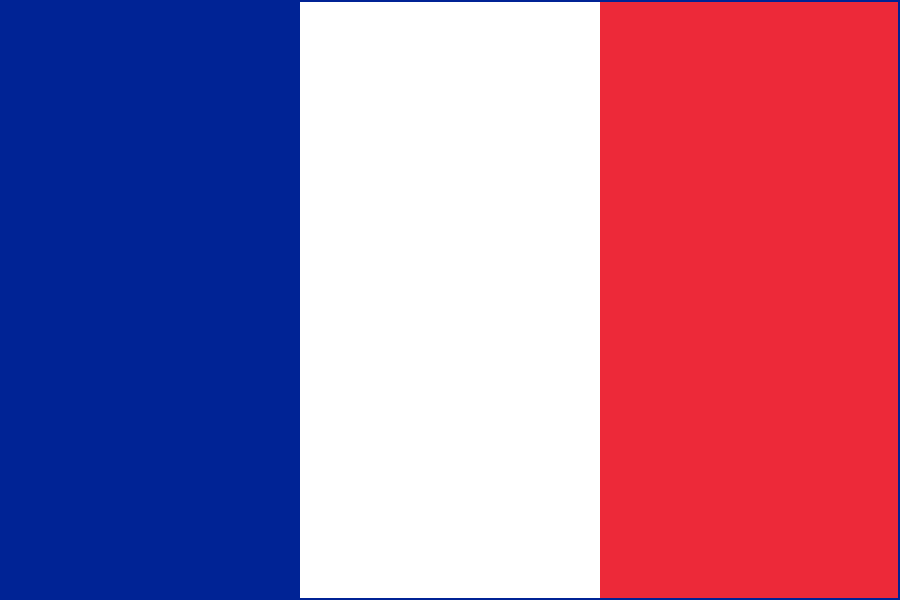
Flag description:
three equal vertical bands of blue (hoist side), white, and red; known as the “Le drapeau tricolore” (French Tricolor), the origin of the flag dates to 1790 and the French Revolution when the “ancient French color” of white was combined with the blue and red colors of the Parisian militia; the official flag for all French dependent areas
note: the design and/or colors are similar to a number of other flags, including those of Belgium, Chad, Cote d’Ivoire, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, and Netherlands
National symbol(s):
Gallic rooster, fleur-de-lis, Marianne
National anthem:
name: “La Marseillaise” (The Song of Marseille)
Economy
Economy – overview:
The French economy is diversified across all sectors. The government has partially or fully privatized many large companies, including Air France, France Telecom, Renault, and Thales. However, the government maintains a strong presence in some sectors, particularly power, public transport, and defense industries. With at least 82 million foreign tourists per year, France is the most visited country in the world and maintains the third largest income in the world from tourism.
France’s leaders remain committed to a capitalism in which they maintain social equity by means of laws, tax policies, and social spending that mitigate economic inequality. France’s real GDP stagnated in 2012 and 2013. The unemployment rate (including overseas territories) increased from 7.8% in 2008 to 10.2% in 2013. Youth unemployment in metropolitan France decreased from a high of 25.4% in the fourth quarter of 2012 to 22.8% in the fourth quarter of 2013. Lower-than-expected growth and high spending have strained France’s public finances. The budget deficit rose sharply from 3.3% of GDP in 2008 to 7.5% of GDP in 2009 before improving to 4.1% of GDP in 2013, while France’s public debt rose from 68% of GDP to nearly 94% over the same period. In accordance with its EU obligations, France is targeting a deficit of 3.6% of GDP in 2014 and 2.8% in 2015.
The administration of President Francois HOLLANDE has implemented greater state support for employment, the separation of banks’ traditional deposit taking and lending activities from more speculative businesses, increasing the top corporate and personal tax rates, including a temporary 75% tax on wages over one million euros, and hiring an additional 60,000 teachers during his five-year term. In January 2014 HOLLANDE proposed a “Responsibility Pact” aimed primarily at lowering labor costs in return for businesses’ commitment to create jobs. Despite stagnant growth and fiscal challenges, France’s borrowing costs have declined in recent years because investors remain attracted to the liquidity of France’s bonds.
GDP (purchasing power parity):
$2.276 trillion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 10
$2.269 trillion (2012 est.)
$2.268 trillion (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
GDP (official exchange rate):
$2.739 trillion (2013 est.)
GDP – real growth rate:
0.3% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 190
0% (2012 est.)
2% (2011 est.)
GDP – per capita (PPP):
$35,700 (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
$35,800 (2012 est.)
$36,000 (2011 est.)
note: data are in 2013 US dollars
Gross national saving:
18.2% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
17.6% of GDP (2012 est.)
19% of GDP (2011 est.)
GDP – composition, by end use:
household consumption: 57.6%
government consumption: 25.1%
investment in fixed capital: 18.7%
investment in inventories: 0.1%
exports of goods and services: 27.3%
imports of goods and services: -28.8%
(2013 est.)
GDP – composition, by sector of origin:
agriculture: 1.9%
industry: 18.7%
services: 79.4% (2013 est.)
Agriculture – products:
wheat, cereals, sugar beets, potatoes, wine grapes; beef, dairy products; fish
Industries:
machinery, chemicals, automobiles, metallurgy, aircraft, electronics; textiles, food processing; tourism
Industrial production growth rate:
-0.4% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 170
Labor force:
29.94 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
Labor force – by occupation:
agriculture: 2.9%
industry: 20.6%
services: 76.4% (2012 est.)
Unemployment rate:
10.2% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
10.2% (2012 est.)
note: includes overseas territories
Population below poverty line:
7.9% (2011)
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
lowest 10%: 3.5%
highest 10%: 25.4% (2011)
Distribution of family income – Gini index:
30.6 (2011)
country comparison to the world: 117
27.9 (1996)
Budget:
revenues: $1.41 trillion
expenditures: $1.522 trillion (2013 est.)
Taxes and other revenues:
51.5% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 11
Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):
-4.1% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 150
Public debt:
93.4% of GDP (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
90.2% of GDP (2012 est.)
note: data cover general government debt, and includes debt instruments issued (or owned) by government entities other than the treasury; the data include treasury debt held by foreign entities; the data include debt issued by subnational entities, as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement, medical care, and unemployment; debt instruments for the social funds are not sold at public auctions
Fiscal year:
calendar year
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
0.9% (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
2% (2012 est.)
Central bank discount rate:
0.75% (31 December 2013)
country comparison to the world: 114
1.75% (31 December 2010)
note: this is the European Central Bank’s rate on the marginal lending facility, which offers overnight credit to banks in the euro area
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
3.1% (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 166
3.44% (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of narrow money:
$810.1 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$738.8 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
note: see entry for the European Union for money supply in the euro area; the European Central Bank (ECB) controls monetary policy for the 17 members of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU); individual members of the EMU do not control the quantity of money circulating within their own borders
Stock of broad money:
$2.299 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$2.273 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of domestic credit:
$3.687 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 6
$3.631 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
Market value of publicly traded shares:
$1.762 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$1.538 trillion (31 December 2011)
$1.983 trillion (31 December 2010 est.)
Current account balance:
-$58.97 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 188
-$45.22 billion (2012 est.)
Exports:
$578.6 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$567.1 billion (2012 est.)
Exports – commodities:
machinery and transportation equipment, aircraft, plastics, chemicals, pharmaceutical products, iron and steel, beverages
Exports – partners:
Germany 16.7%, Belgium 7.5%, Italy 7.5%, Spain 6.9%, UK 6.9%, US 5.6%, Netherlands 4.3% (2012)
Imports:
$659.8 billion (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$653.4 billion (2012 est.)
Imports – commodities:
machinery and equipment, vehicles, crude oil, aircraft, plastics, chemicals
Imports – partners:
Germany 19.5%, Belgium 11.3%, Italy 7.6%, Netherlands 7.4%, Spain 6.6%, UK 5.1%, China 4.9% (2012)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
$198.7 billion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 14
$188.4 billion (31 December 2011 est.)
Debt – external:
$5.371 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 5
$5.004 trillion (31 December 2011)
Stock of direct foreign investment – at home:
$1.103 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 7
$1.095 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
Stock of direct foreign investment – abroad:
$1.489 trillion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 4
$1.497 trillion (31 December 2012 est.)
Exchange rates:
euros (EUR) per US dollar –
0.7634 (2013 est.)
0.7752 (2012 est.)
0.755 (2010 est.)
0.7198 (2009 est.)
0.6827 (2008 est.)